Dangerous Original Antigenic Sin Anticipated in SARS-CoV-2
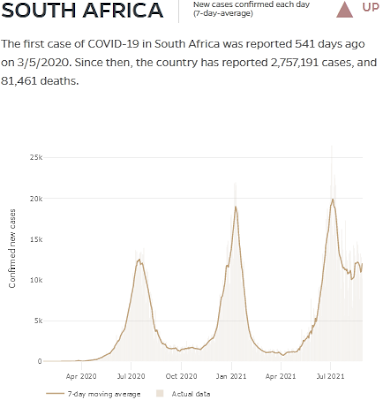
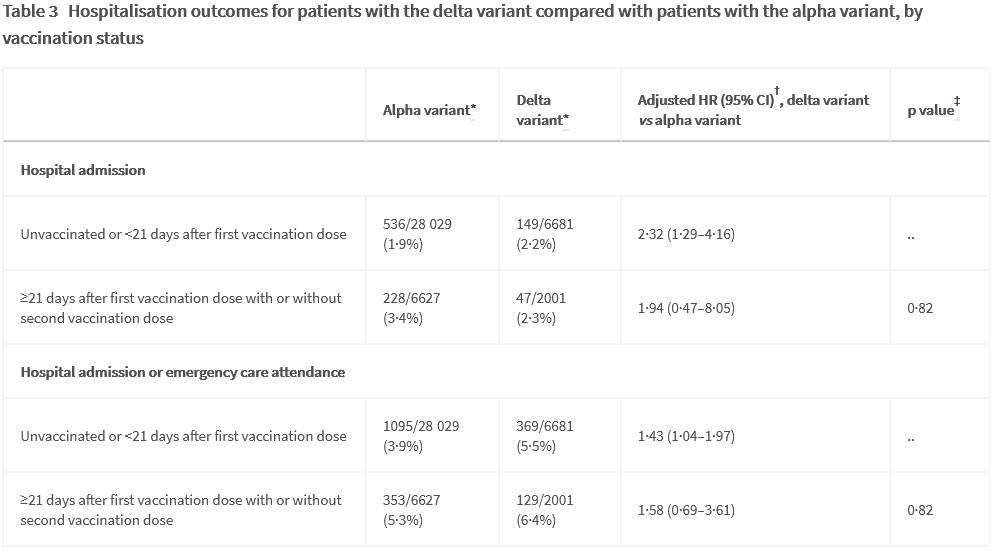
Disclaimer : This is an opinion and a prediction that includes as many sources and the best logic possible. Do not base your personal health decisions on it. Plain Language Introduction SARS-CoV-2 is a novel virus with its closest relatives in bats, emerging in the human population at some point in late 2019. As a newly introduced pathogen, there was only one variant at first. Now we have thousands of strains that have been identified, with countless individual virus particles with countless mutations. The genetic diversity of SARS-CoV-2 is much greater than scientists thought it would be by this point in time. Recombination and Evolution That's because we failed to notice that SARS-CoV-2 relies heavily on recombination for evolution. With recombination, in a host that is infected with two strains of the virus, the virus can effectively create a child from two parent virions(a virion is a single virus) through a process called strand switching. When creating a new vi...